Introduction:
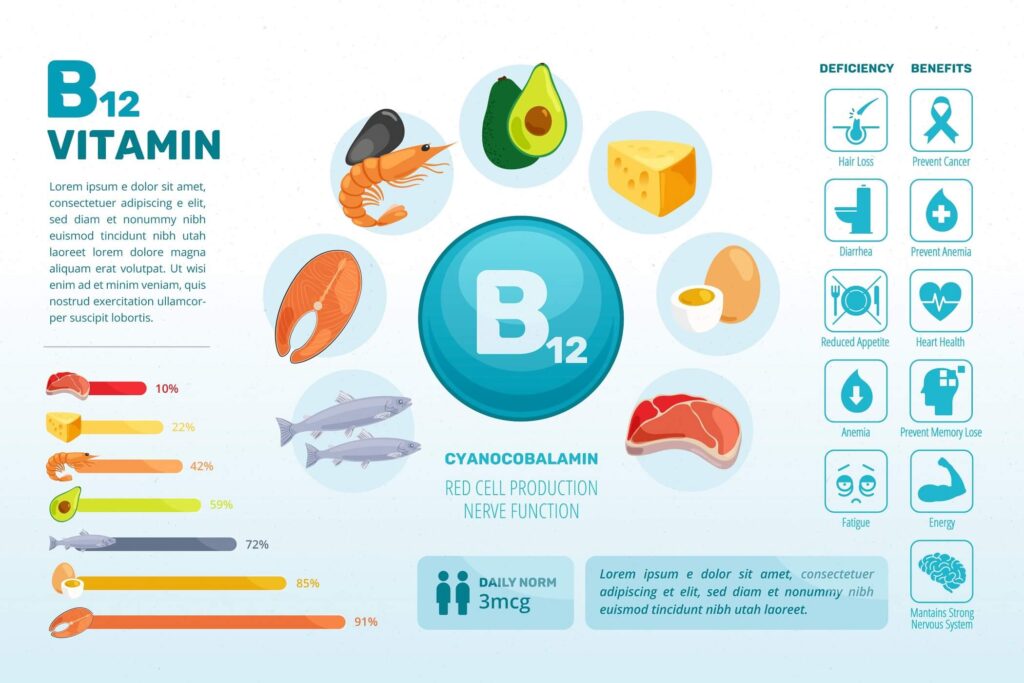
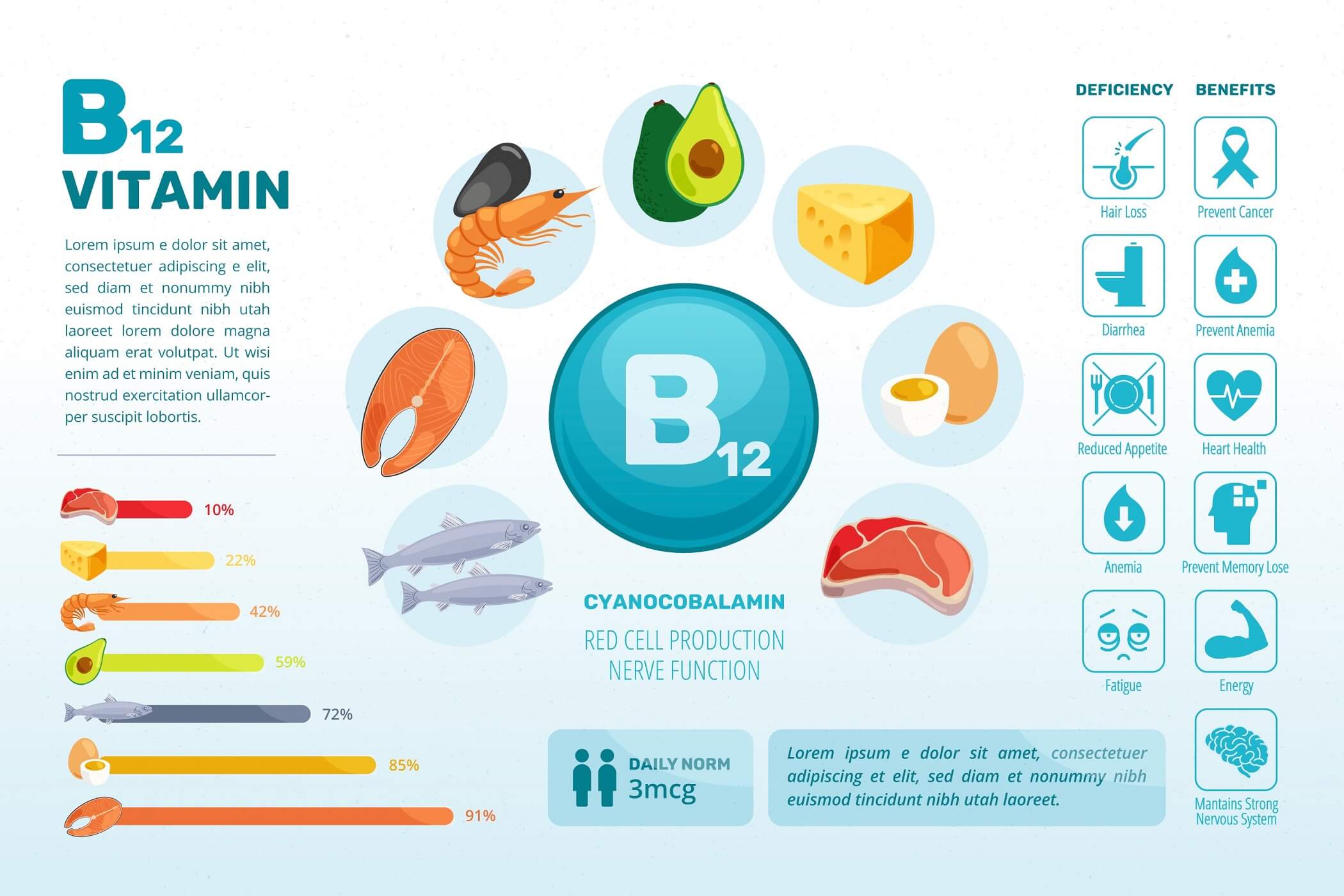
Vitamin B12 is also referred to as cobalamin, is an essential nutritional element that plays an essential role in many bodily functions. From promoting nerve health to assisting in the creation Red blood cells as well as DNA, the B12 vitamin is vital for general well-being. But, deficiency of B12 can cause several health issues. In this article we’ll look at the signs of the condition, its effects, diet sources, and treatments to treat Vitamin B12 insufficiency.
Knowing Vitamin B12 Insufficiency
Vitamin B12 is found primarily in animal products, such as fish, meat eggs, dairy, and other fish. Thus, those who follow the vegan or vegetarian diet, and those suffering from certain health conditions that affect the absorption of nutrients are more prone to a deficiency of B12. In addition, those who are elderly could have a higher risk because of a lower digestion of stomach acids. This is vital for absorption of B12.
Signs and symptoms for Vitamin B12 Insufficiency
- Weakness and fatigue: B12 is vital in the creation red blood cells. These cells are which are responsible for transporting oxygen around the entire body. Deficiency could cause anemia that can lead to weakening and fatigue.
- Neurological issues: B12 is essential for the maintenance of the health of nerve cells. Deficiency can lead to symptoms like numbness discomfort walking, and tingling that can escalate into more serious neurological issues when left untreated.
- Cognitive Impairment A few people suffering from B12 deficiencies might suffer from memory loss, trouble concentration, and other cognitive problems.
- Jaundiced or pale skin: Anemia resulting from B12 deficiencies can cause pale or jaundiced skin which indicates a deficiency in healthy blood red cells.
The effects from Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Beyond the immediate signs Long-term B12 deficiency could have severe negative consequences. Long-term neurological damage, which includes irreparable nerve damage, could be a risk. If left untreated, anemia could result in cardiovascular problems that affect the heart and circulatory system.
Dietary sources for Vitamin B12:
Although B12 is found primarily within animal foods, there is other sources for those on the vegan or vegetarian diet. They include:
- Fortified Foods Certain plant-based food items like cereals and plant-based milk are fortified with B12.
- Supplements Supplements for B12 are readily available and may be beneficial for people with diet restrictions or issues with absorption.
Treatment for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Dietary changes: Include B12-rich food items in the diet is an important step. Non-vegetarians should include chicken, fish, meat as well as dairy products.
- Supplementation B12 supplementation, available in a variety of forms (pills or injections or tablets sublingual) are effective solutions to deficiencies.
- Intramuscular Injections In extreme cases in which absorption is compromised Healthcare professionals may suggest B12 injections to aid in faster and more effective absorption.
Conclusion:
Vitamin B12 insufficiency can be a major health issue which can have a profound impact on the various bodily functions. Understanding the signs, recognizing the potential effects and taking suitable dietary and treatment strategies are vital steps in addressing and prevent B12 deficiency. Through dietary modifications supplements or interventions, taking care to address B12 deficiency quickly is crucial for ensuring the best health and wellbeing. Always consult a medical expert for advice and assistance.